Electricity powers all that we have around us from lights and fans to huge machines. But when the flow of current is excessive it damages devices or leads to short circuits. In order to prevent that we use MCB which means Miniature Circuit Breaker.
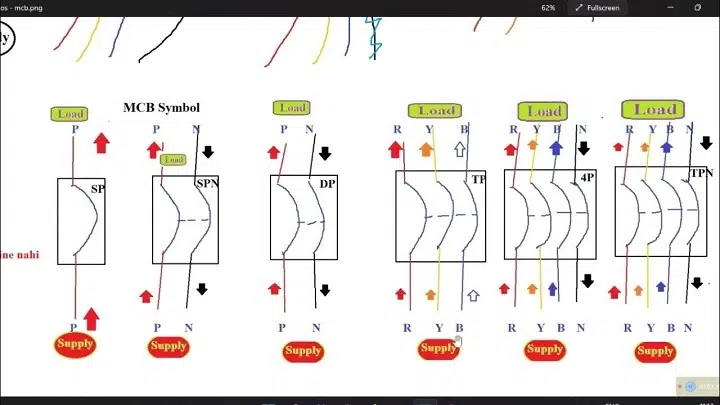
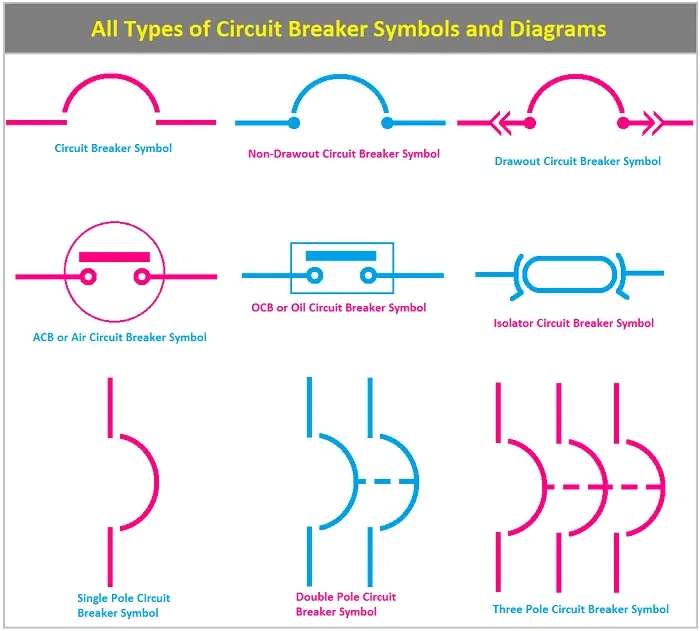
In circuit schematics MCBs are represented using distinctive symbols that make it easy to identify them in electrical schematics. The symbols help electricians engineers and students understand where and how a circuit is protected.
What Is an MCB
An MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) is an electric automatic switch that is employed to protect electrical circuits from damage due to overcurrent or short circuit.
If there is excessive current flow through a circuit the MCB automatically cuts off the supply of devices and wiring.
Full form: Miniature Circuit Breaker
Main function: To protect electrical circuits from damage due to overload and short-circuit.
Key features of MCB:
• It automatically acts on fault.
• Can be reset manually once tripped.
• Used in homes, schools and industries.
• Replaces older fuse systems.
Symbol of MCB in Electrical Diagrams
In electrical circuit diagrams all the devices have a distinctive symbol. The MCB symbol is employed to identify points of circuit protection.
MCB diagram symbol is the plain rectangle or box with a lever line or curve. It may have a small arc curve or switch placed above it. The line entry shows the points where current enters and exits.
Standard Representation of MCB Symbol:
________
| |
| __ |
|__/ \__|
This is a generic drawing of a switch in a box showing the circuit may open or close automatically when faults are sensed.
Elements of MCB Symbol
The MCB symbol is not random; all lines in the symbol are symbolic in meaning.
| Component | Purpose | Description | Role |
| Box outline | Casing | Shows the MCB body | Protects internal parts |
| Switch line | Lever or trigger | Used to switch MCB on/off | Manual operation |
| Curved arc | Contact area | Shows where the current flows | Indicates connection |
| Connection points | Input/Output | Shows where the wires are joined | Entry/exit current points |
In technical diagrams one end of the symbol connects to the supply (phase line) and the other connects to the load (like light or fan).
How MCB Works
MCB works on a simple principle; it automatically breaks the circuit when the current rises above the rated value.
It has two kinds of tripping mechanisms:
Thermal Trip:
Works when the current flow is heavy for an extended duration. A bimetal strip heats and bends such that the switch opens.
Magnetic Trip:
Works when there is high current (short circuit) abruptly. An electromagnet is activated and operates a lever to open the circuit instantly.
Once the fault is cleared the MCB can be reset manually to supply power again.
Types of MCB
MCBs come in different forms based on the level of protection provided.
| Type | Trip Curve | Application |
| Type B | Trips between 3 to 5 times rated current | Used for residential and light circuits |
| Type C | Trips between 5 to 10 times rated current | Used for commercial or small industrial applications |
| Type D | Trips between 10 to 20 times rated current | Used for heavy machinery circuits |
They all use the same symbols on diagrams but designations like B10, C16, or D32 represent their rated amperage.
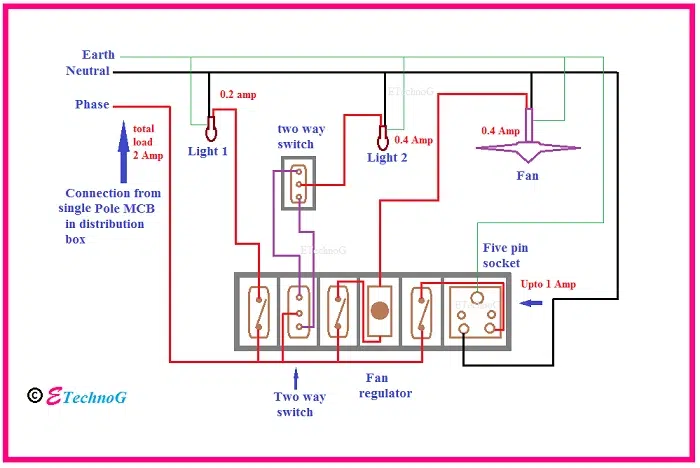
MCB Symbol in Single Line Diagram (SLD)
In the Single Line Diagram (SLD) MCB is drawn between the main power line and the serve line for load.
Example simple diagram:
← Power Source → [ MCB ] → Load
In elaborate diagrams MCBs are drawn with serve name like:
• MCB (C16) for 16A serve
• MCB (B6) for serve of lights
This lets the engineers know about each circuit’s serve rating and position.
Importance of MCB Symbol in Wiring Diagram
MCB symbols on wiring diagrams are important in electrical safety and design.
Why it matters:
• Identifies where the circuit protection is located.
• Facilitates fast fault-finding by electricians.
• Prevents confusion during installation.
• Offers clear documentation for future maintenance.
When you look at a building wiring diagram the MCB symbol tells you which line or switchboard is protected.
Uses of MCB
MCBs are used in virtually all locations where power is being drawn.
Home Electrical Systems
Fixed on distribution boards (DB boxes). Protects light fans and plug circuits.
Offices and Schools
Protects computers, air conditioners and laboratory equipment.
Industries
Used for motors, heavy machinery and control panels.
Shops and Apartments
Used for individual circuits to control different loads.
Renewable Energy Systems
Used in solar systems and inverters to protect against short circuits.
MCB vs Fuse
Though both MCB and fuse perform the same function (circuit protection), they work and are used differently.
| Feature | MCB | Fuse |
| Working | Automatic reset switch | Melts and must be replaced |
| Reusability | Can be reused | Temporary usage only |
| Response time | Slightly delayed | Very fast |
| Convenience | Easy to use | Must be replaced manually |
| Symbol | Switch symbol with enclosure | Zig-zag line or wire symbol |
The symbol of MCB is newer and more complex, representing automatic control in place of a mere wire.
Example of MCB Diagram in Home Circuit
In a domestic wiring circuit which is simple the MCB symbol is placed near the main board or near switches.
Example design:
Main Supply → MCB → Switch → Light/Fan/Plug
Step-by-step action:
- Power from the main line to the MCB.
- MCB allows current to flow under normal conditions when all is safe.
- If a short circuit is detected MCB trips and power is disconnected.
- Once the fault is corrected it can be reset to continue working.
This gives protection to humans as well as equipment.
Also Read: iPhone Symbol for Free Fire: Meaning, Use, and Complete Guide in Simple Words
Marking MCB in a Wiring Diagram
Each MCB in a circuit must be marked for identification.
General marking format:
• MCB-1: Lighting circuit
• MCB-2: Socket circuit
• MCB-3: Air conditioner
• MCB-4: Geyser or washing machine
The marking makes diagrams easier to read and avoids confusion during maintenance.
Safety Precautions While Using MCB
While installing or using MCBs always follow safety precautions.
General safety tips:
• Switch off the main supply before operating.
• Use MCBs of correct rating (amperes).
• Do not reset MCB repeatedly without finding the fault.
• Keep MCB boards dry and free from dust.
• Avoid overloading multiple appliances on one circuit.
Advantages of MCB
MCBs are employed over fuses because of a number of reasons:
- Easy reset upon fault
• Stable and secure operation
• Fault detection with accuracy
• Longer lifespan
• Compact and neat structure
• Avoids short circuit as well as overload
These advantages make them an essential part of every modern-day electrical system.
Simple Diagram Example
Following is a simple example of how MCB symbols appear in an electrical diagram:
[Main Power]
|
[MCB C16]
|
[Light Switch]
|
[Bulb]
This little symbol within the diagram suggests that before the power is supplied to the bulb, it is first passed through an MCB for protection.
The MCB symbol is one of the most important symbols of an electrical diagram. It represents protection and safety control. Knowledge of the symbol helps you to read circuit diagrams to determine faults and design safe wiring systems.
An MCB may be plain to look at but its symbol expresses importance, automatic protection, reset feature, and modern-day safety.
Whether you are an apprentice electrician or pupil studying, the MCB symbol is a vital step to achieving skill in circuit diagrams. Not only does it tell us how electricity travels but also how we guide and protect it safely on a daily basis.