When you are learning electronics or building a simple circuit, you see the NPN transistor symbol on a regular basis. The NPN transistor is perhaps one of the most common electronics devices used in switching and amplification. The symbol for the transistor is very simple but very insightful because it indicates the direction of the current inside the transistor.
Understanding the NPN transistor symbol assists in comprehending circuit diagrams, correct connection of the components, and determination of the direction of flow of electricity within the system. Here, in this article, we have described what an NPN transistor is, its symbol, and operation in simple language to comprehend.
What Is an NPN Transistor
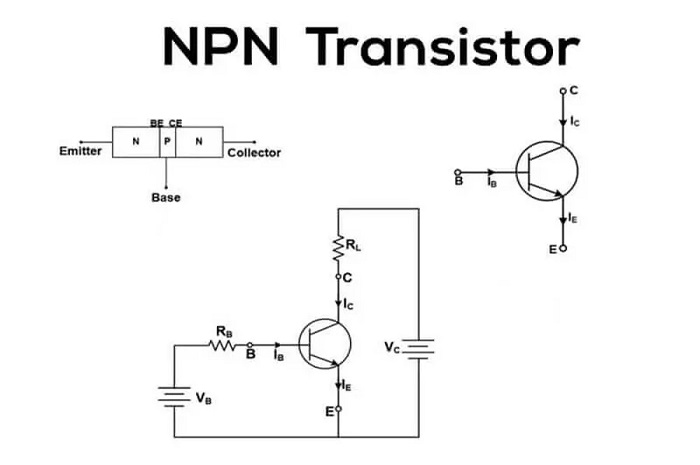
An NPN transistor is a BJT. It has three layers of semiconductor, two N-type and one P-type in between.
An NPN transistor has three terminals:
- Emitter (E) – emits electrons
- Base (B) – controls the flow of electrons
- Collector (C) – collects electrons
A small current into the base allows a larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter in an NPN transistor.
Basic Meaning of NPN
- N – Negative (electron-rich layer)
- P – Positive (hole-rich layer)
- N – Negative (electron-rich layer again)
Therefore, the structure is N-P-N.
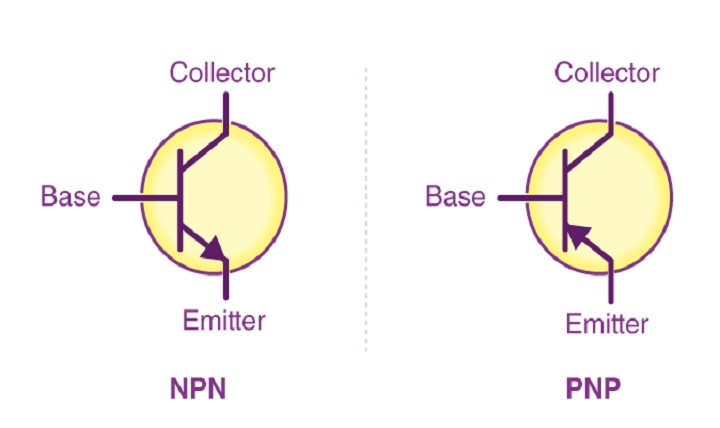
Symbol of NPN Transistor
The symbol of an NPN transistor is quite simple to recognize if you know what each section represents.
Components of Symbol:
- Three lines represent the Collector (C), Base (B), and Emitter (E).
- The arrow is marked on the emitter leg.
- The direction of the arrow is outward, which indicates normal current direction.
Key NPN Symbol Features:
- The arrow is pointing away (from emitter to base).
- The collector is on the top.
- The emitter is on the bottom.
- The base is in the middle.
Memory Device to Recollect:
“NPN — Not Pointing iN” (the arrow is not pointing inside).
That makes you recall that for an NPN transistor, the arrow is pointing outside.
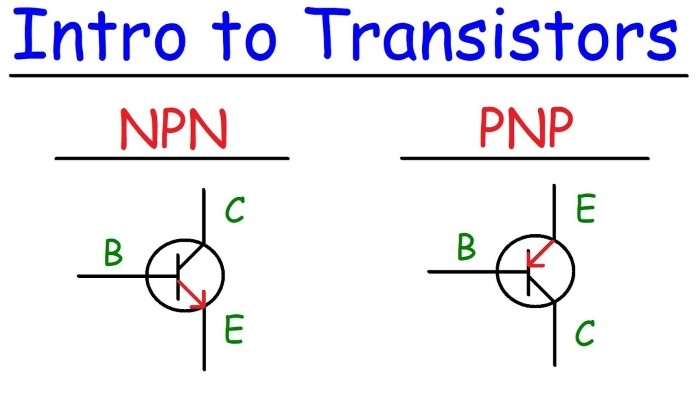
Visual Representation of Symbol
The symbol of an NPN transistor looks like this in drawings:
C
|
|
|\
| \
B —-| \
| \
|—->
Where the arrow (→) is pointed away from us, i.e., base to emitter flow of current.
Learning Each Terminal
Collector (C):
- Gathers electrons from the emitter through the base.
- Generally connected to the positive side of the circuit through a resistor or load.
Base (B):
- Thin middle section that controls the transistor.
- Little current here controls the large current between collector and emitter.
Emitter (E):
- Siphons electrons out into the base region.
- In this terminal the direction of current flow can be shown through an arrow.
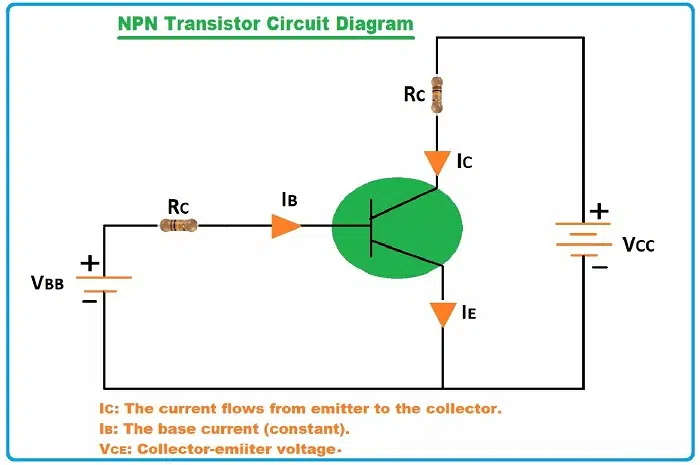
NPN Transistor Working
The NPN transistor acts as a current amplifier and the collector current is controlled by a very small base current.
Procedure
- When a very small positive voltage is applied to the base then current can be possible between the emitter and the collector.
- The electrons which are present in the emitter travel to the collector.
The base acts as a gate to regulate the current passing through it.
Operational Condition:
- The base-emitter junction has to be forward biased. A positive voltage is applied at the base.
- The collector-base junction should be reverse biased.
In short words:
When the base is ON (is receiving signal), current flows from collector to emitter.
Current doesn’t flow when the base is OFF.
How to Identify NPN Symbol in a Circuit
You can tell the NPN symbol in a circuit at a glance by looking at the direction of the arrow.
Arrow pointing outward – NPN transistor.
Arrow pointing inward – PNP transistor.
That’s all there is to it.
Difference Between NPN and PNP Symbols
| Feature | NPN Transistor | PNP Transistor |
| Direction of Arrow | Toward outward | Toward inward |
| Current Flow | From collector to emitter | From emitter to collector |
| Base Current | Positive | Negative |
| Symbol Reminder | “Not Pointing iN” | “Points iN” |
| General Usage | Digital circuits | Analog circuits |
Why NPN Transistors Are Popular
NPN transistors have higher usage in a circuit compared to PNP transistors due to the following reasons:
- They have higher electron mobility.
- Easy to handle positive voltage circuits.
- Can work correctly in both switching and amplifier circuits.
- Good for microcontrollers and logic circuits.
Application of NPN Transistor
NPN transistors are widely utilized in most electrical and electronic circuits.
- Switching Applications
They act as electronic switches for trying to turn on and off devices.
Example: Switching LEDs, relays, or motors.
- Amplifier Circuits
They are used to demagnify big signals to small signals in sound devices or speakers.
- Logic Circuits
They are used in computers, digital circuits, and logic gates.
- Sensor Circuits
They are used in light, movement, and temperature sensors.
- Power Regulation
They regulate current and voltage in power supply units.
Symbol Variations in Circuit Diagrams
In other books or computer software, the symbol of an NPN transistor might look a bit different but with the same format:
- Three terminals (C, B, E)
- Outward arrow on emitter
- Straight and sloping lines connecting the terminals
Transistors, in complex diagrams, are addressed by symbols such as Q1, Q2, or T1.
Example in a Circuit Diagram
Suppose you wish to turn on an LED using a transistor switch.
Parts:
- NPN Transistor (e.g., BC547)
- LED
- Resistor
- Battery
Connections:
- Emitter to ground.
- Collector to one LED terminal.
- Other LED terminals to positive voltage through a resistor.
- Base to a small voltage through another resistor.
If there is a small current into the base, the LED will be on. If there is no current into the base, the LED will be off.
Current Direction Flow in NPN Symbol
In an NPN transistor:
- Current flows from collector to emitter.
- Electrons flow from emitter to collector.
- Direction of normal current (outward) is indicated by the arrow in the emitter.
Mathematical Relationship
Mathematical relationship of collector, base, and emitter current is as follows:
Ic = β × Ib
Ie = Ic + Ib
Where:
- Ic = Collector current
- Ib = Base current
- Ie = Emitter current
- β = Amplification factor (current gain)
This means that a very small base current is able to provide a much higher collector current.
Practical Tip to Help You Memorize Symbol Direction
In drawing or identifying the symbol:
- The arrow on the emitter points away from NPN.
- The middle line is always the base.
- The top line is the collector.
Quick test:
If you can say “Current goes Not Pointing iN,” it’s NPN.
Advantages of NPN Transistors
- Easy to use.
- High switching speed.
- Suitable for most positive logic circuits.
- Cheap and available in large numbers.
- Good gain at low base current.
Disadvantages
- Must be biased carefully for the base.
- Restricted to low current use in small models.
- Requires additional parts to operate reliably.
Common Examples of NPN Transistors
- BC547
- 2N2222
- BD139
- TIP120
- C1815
These are used normally in small electronic kits and printed circuit boards.
Important Safety Instructions
Connect the transistor in the proper direction always. Wrong pin connection kills it. Check datasheets to see pin numbers for collector, base, and emitter.
Summary Table of NPN Transistor Symbol Meaning
| Symbol Part | Meaning | Function |
| Arrow | Indicates current flow direction | Leads out |
| Collector | Collects electrons | Staggers to the load |
| Base | Controls current | Signal input |
| Emitter | Emit electrons | Ground point |
| Lines | Define terminals | Visual cue |
Apt Facts About NPN Transistor Symbol
- The direction of the arrow was meant to mirror conventional current flow.
- The symbol enables engineers to instantly identify the type of transistor.
- Analog and digital circuits share the same symbol in PCB design.
- It is the best-known electronic symbol other than resistor and capacitor.
The NPN transistor symbol is simple but helpful. The arrow pointing away indicates current flow, and the three terminals indicate how power and control are blended inside the device. Recognition of the symbol keeps it easy for beginners to read and build circuits.
In millions of electronic devices, an NPN transistor is implemented as a switch and amplifier. An NPN transistor is used in computer processors and LED circuits.
From remembering that the arrow on the symbol “points out,” you can easily identify and utilize NPN transistors in your electronic projects.